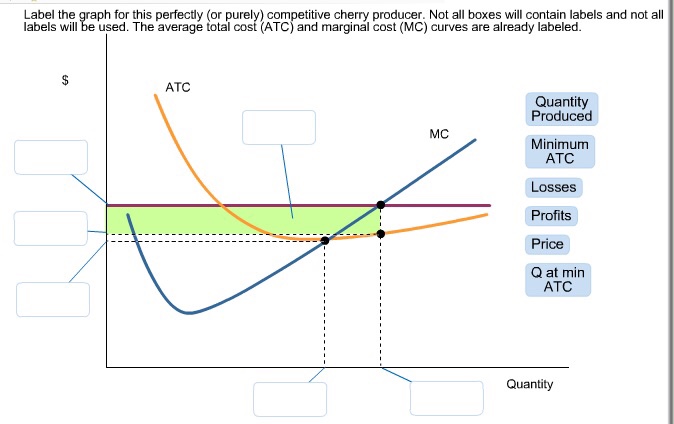
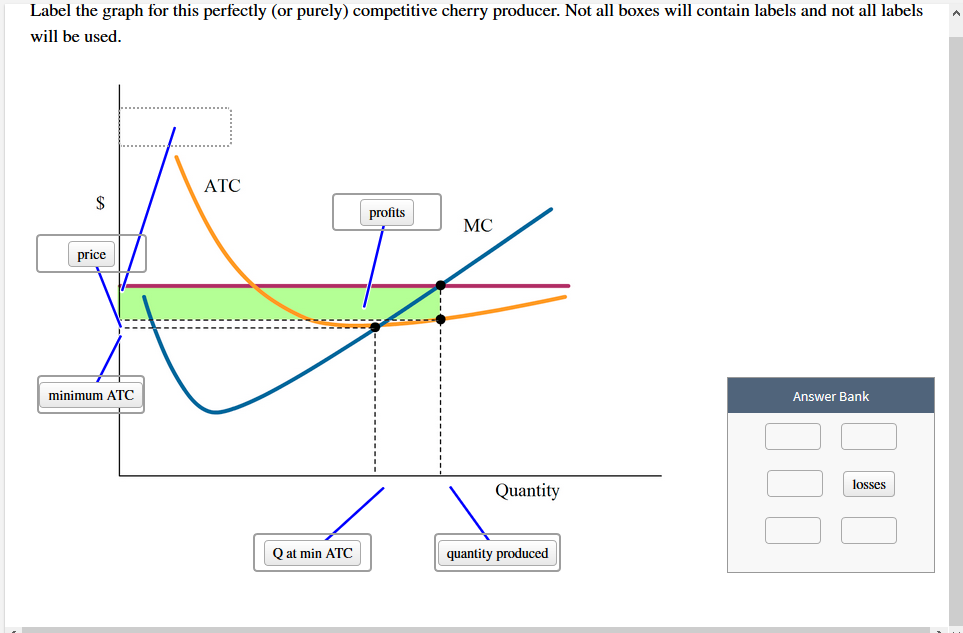
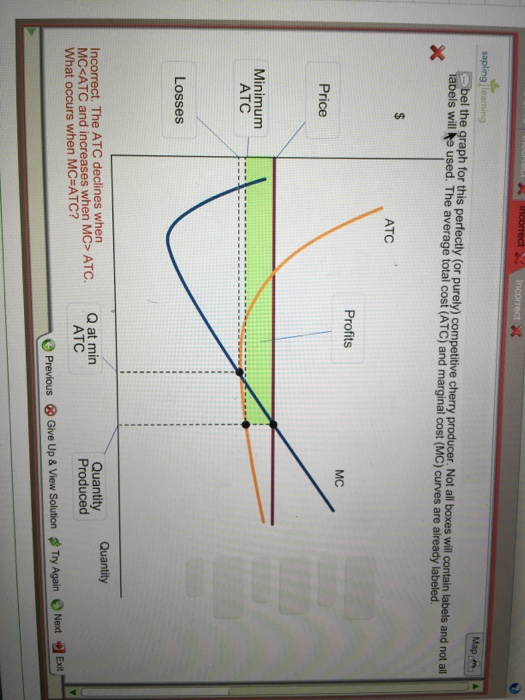
40 label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. not all of the labels will be used.
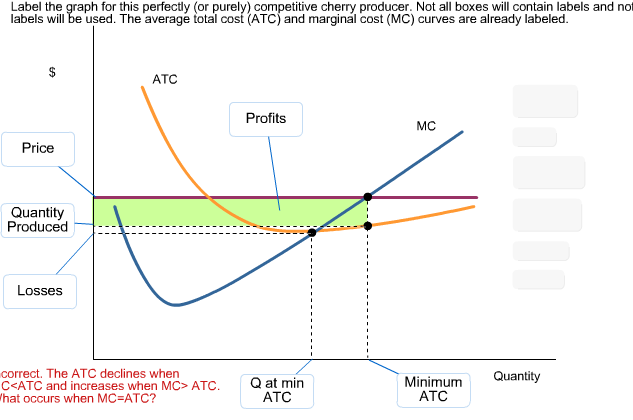
Perfectly Competitive Market Equilibrium (With Diagram) A perfectly competitive market is one in which the number of buyers and sellers is very large, all engaged in buying and selling a homogeneous product without any artificial restrictions and possessing perfect knowledge of market at a time. There are two parties which bargain in such a market, the buyers and the sellers. Solved Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) | Chegg.com Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. Not all boxes will contain labels and not all labels will be used. ATC profits profits MC price minimum ATC Answer Bank Quantity losses Q at min ATC quantity produced Question: Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer.
weblogin idpz | University of Toronto The Chrome browser, in particular, now maintains cookies even after exiting. This enables you continue where you left off. While convenient, it conflicts with the intent of session cookies: exiting your browser should clear all of your session cookies ensuring no one can access your application privileges.
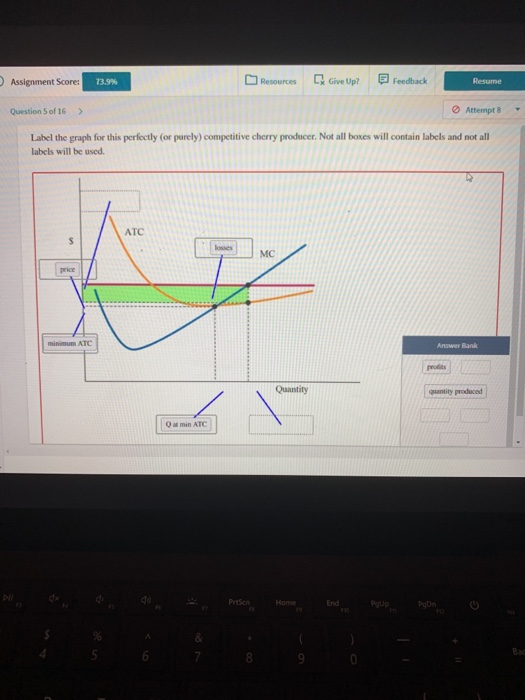
Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. not all of the labels will be used.
PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market - Eastern Mediterranean University 2) Prices in perfectly competitive markets are determined by the interaction of demand and supply. Once the equilibrium price is determined, all the buyers and sellers have to accept it if they want to buy or sell in perfectly competitive markets. i.e. All the firms and consumers are price takers. They cannot affect the market price. See graph ... PDF AP MICROECONOMICS 2015 SCORING GUIDELINES - College Board The student earned 1 point in part (b)(i) for correctly drawing a graph for the perfectly competitive market an d correctly labeling the market price, P m , and quantity, Q m The student earned 1 point in part (b)(ii) for correctly identifying the firm's profit -maximizing quantity at marginal cost (MC) equal to price or average revenue. ECON 150: Microeconomics - Brigham Young University-Idaho In the perfect or pure competition market, there are a large number of firms each producing the same product (as called a standardized or homogeneous product). Since the number of firms is very large, no one firm can influence the market price, thus each firm has no market power and each is a price taker.
Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. not all of the labels will be used.. Exam 3 Assignments/Quizzes/In-Class (Chapters 11 - 14) The graph shows Mauricio's initial budget constraint. The price per unicycle is $120 and per monkey is $90. Using the graph, show what happens to Mauricio's budget line when the price of unicycles increases to $180. What is Mauricio's budget for monkeys and unicycles? Mauricio's budget: $720 Kimiko is planning a party to celebrate her birthday. Micro Chapter 8 Perfect Competition Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operatin and producing cherries. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. There are more labels than boxes. The average total cost (ATC), marginal cost (MC), and marginal revenue (MR) curves are already labeled. Labels. 1. Q at min ATC 2. Q profit max 3. (Solved) - Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive ... Label the graph for this perfectly ... Solved Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) | Chegg.com Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. Not all boxes will contain labels and not labels will be used. The average total cost (ATC) and marginal cost (MC) curves are already labeled. Question: Label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer.
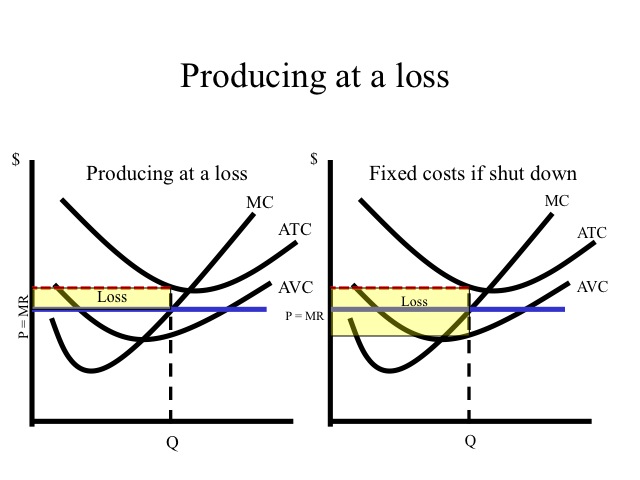
[Solved] Please help me on this question | Course Hero The graph is shown below Step-by-step explanation The perfectly competitive firm sets P=MC for profit maximization and produces the Quantity produced The price is constant whereas the ATC is less than the Price so the firm is making a positive profit. The ATC at Q produced and minimum ATC are shown where the quantity produced is also shown. ECON 150: Microeconomics - Brigham Young University-Idaho In the perfect or pure competition market, there are a large number of firms each producing the same product (as called a standardized or homogeneous product). Since the number of firms is very large, no one firm can influence the market price, thus each firm has no market power and each is a price taker. PDF AP MICROECONOMICS 2015 SCORING GUIDELINES - College Board The student earned 1 point in part (b)(i) for correctly drawing a graph for the perfectly competitive market an d correctly labeling the market price, P m , and quantity, Q m The student earned 1 point in part (b)(ii) for correctly identifying the firm's profit -maximizing quantity at marginal cost (MC) equal to price or average revenue. PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market - Eastern Mediterranean University 2) Prices in perfectly competitive markets are determined by the interaction of demand and supply. Once the equilibrium price is determined, all the buyers and sellers have to accept it if they want to buy or sell in perfectly competitive markets. i.e. All the firms and consumers are price takers. They cannot affect the market price. See graph ...






![PDF] A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis ...](https://researchain.net/static/img/step.jpg)
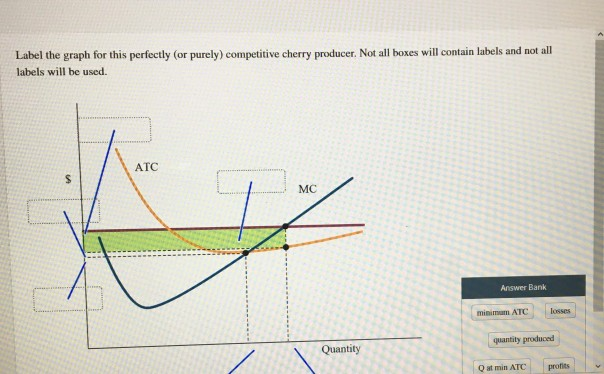









Post a Comment for "40 label the graph for this perfectly (or purely) competitive cherry producer. not all of the labels will be used."